Your Customer Data is Your Most Valuable Asset
Customer Data Correction Examples
Whether it's an incomplete name, misspelled name, wrong address, partial address, or any other inaccuracy, XceleratedONE™ can find the correct information and push it back into your DMS all while you focus on what you do best (or take a nap!). See the image below for actual examples of data deficiencies we've fixed.
.png)
-
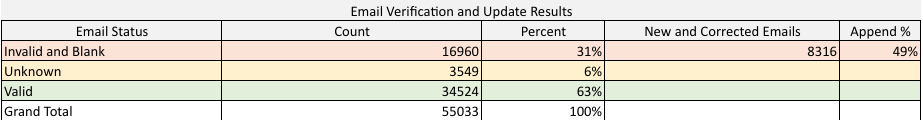
Analysis of Dealer Data - (From a CDP, Marketing Platform or DMS)
- Flag / Remove INVALID Emails (31%)
- Corrected and updated emails to invalid and blank (49%)
- Updated customers that have moved (12%)
- Fix addresses that are not updated by NCOA (51% of 9,753)
- Append distance your customers live from your dealership (80% of your customers live within 25 miles)
- Add new and/or changed cell phone numbers (8%)
Email Addresses
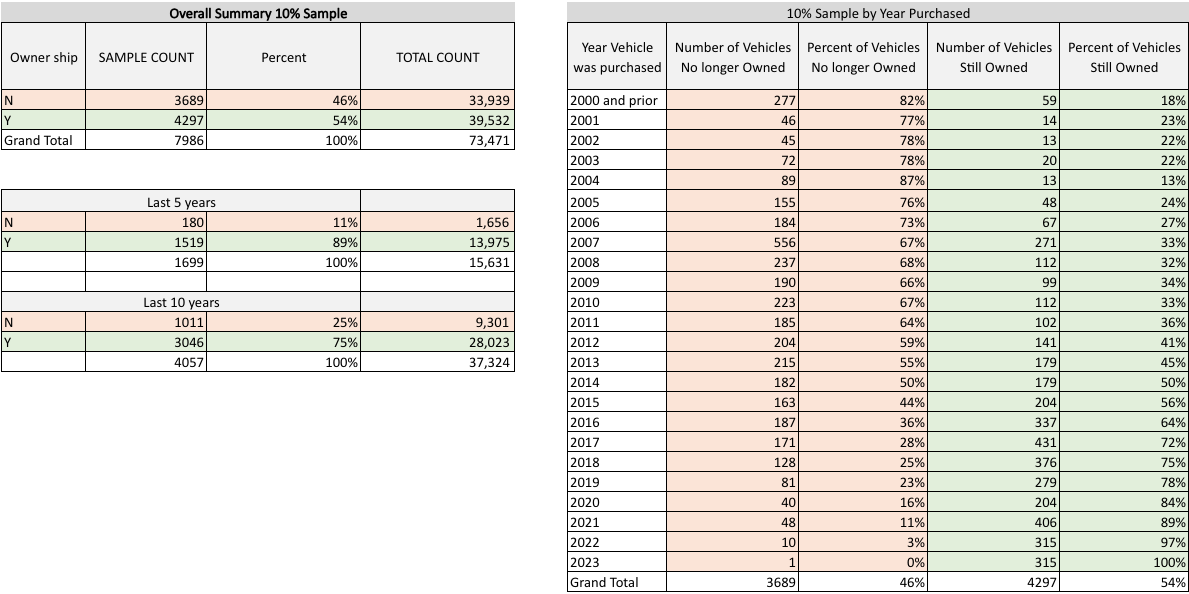
No Longer Owned Vehicles
Ask For More Examples
Unlock the Possibilities
Schedule a quick call with us, and let's explore how XceleratedONE™ can elevate your customer data.
Plus, enjoy a complimentary demonstration with a sample of your actual data to get a taste of what we can offer.
Book your slot now!
To best view this image, turn your device sideways and use two fingers to zoom until it fits your screen.
Key Reasons Your Customer Data is Inaccurate:
User Input Errors:
Users may make mistakes when providing information, such as typos, misspellings, or entering incorrect details. These errors can propagate throughout the database and compromise the accuracy of the data.
Changing Customer Information:
Customer details change over time, including addresses, email addresses, phone numbers, and other personal information. Failure to update this information can result in outdated and inaccurate records.
Incomplete Data:
Users may not provide all the required information, leading to incomplete records. Incomplete data hinders a comprehensive understanding of customers and can limit the effectiveness of marketing and communication efforts.
Data Decay:
Over time, the relevance and accuracy of certain data points may diminish. People change jobs, move to new locations, or switch email addresses, leading to outdated information in the database.
Duplicate Entries:
Duplicate records can emerge from various sources, such as users creating multiple accounts, technical glitches, or errors during data entry. Duplicate entries can inflate user counts and distort analytics.
Lack of Regular Updates:
Without a systematic process for regular updates, first-party data can quickly become obsolete. Businesses that do not actively maintain and refresh their databases are more prone to inaccurate information.
Integration Issues:
When integrating data from various sources or systems, inconsistencies can arise. Mismatched formats, conflicting data structures, or errors in data transfer processes can introduce inaccuracies.
User Privacy Settings:
Privacy-conscious users may provide limited or false information to protect their privacy. While respecting user privacy is essential, it can result in incomplete or inaccurate data for certain individuals.
System Glitches and Technical Errors:
Technical issues within the data collection, storage, or retrieval systems can introduce errors. These glitches may lead to data corruption, loss, or other inaccuracies.
Employee Error:
Human error during data entry or management processes, whether in customer support, sales, or other departments, can contribute to inaccuracies in first-party data.
Competitive Advantage:
Businesses that effectively leverage their first-party data gain a competitive edge. The ability to offer personalized experiences and targeted marketing campaigns based on real customer insights sets a brand apart in the marketplace.
Compliance and Trust:
First-party data is collected directly from customers with their consent, which helps businesses adhere to data protection regulations. Prioritizing privacy and transparency builds trust with customers, which is essential in today's data-conscious environment.
Why your customer data is valuable:
Customer Understanding:
The information you collect of your customers or subscribers (aka: First Party Data) provides direct insights into customer behaviors, preferences, and interactions with a brand. This deep understanding enables businesses to tailor products, services, and marketing strategies to meet the specific needs and expectations of their audience.
Personalization:
Personalization is a key driver of customer engagement. First-party data allows businesses to create personalized experiences, such as targeted marketing campaigns, customized product recommendations, and individualized communication, fostering stronger connections with customers.
Marketing Effectiveness:
Leveraging first-party data enhances the precision and effectiveness of marketing efforts. Marketers can segment their audience based on actual behaviors and preferences, delivering more relevant and timely messages. This targeted approach often leads to higher conversion rates and improved return on investment.
Product and Service Improvement:
By analyzing first-party data, businesses can identify areas for improvement in their products or services. Feedback from customers, their purchasing patterns, and satisfaction levels can inform strategic decisions and drive continuous innovation.
Customer Retention:
Understanding customer behaviors and preferences helps in creating loyalty programs, personalized incentives, and retention strategies. This fosters customer loyalty, reduces churn, and contributes to the long-term success of the business.
Operational Efficiency:
First-party data can be used to streamline internal operations. Whether it's inventory management, order fulfillment, or customer support, having accurate and timely data improves efficiency and reduces operational costs.
Competitive Advantage:
Businesses that effectively leverage their first-party data gain a competitive edge. The ability to offer personalized experiences and targeted marketing campaigns based on real customer insights sets a brand apart in the marketplace.
Compliance and Trust:
First-party data is collected directly from customers with their consent, which helps businesses adhere to data protection regulations. Prioritizing privacy and transparency builds trust with customers, which is essential in today's data-conscious environment.
Adaptability to Changes:
As marketing channels, consumer preferences, and technologies evolve, businesses with a solid foundation of first-party data can more easily adapt to changes. This adaptability is crucial for staying relevant and competitive in dynamic markets.
Risk Mitigation:
Relying on first-party data reduces dependence on third-party data sources, mitigating the risks associated with data quality issues, inaccuracies, or changes in external data regulations.
Competitive Advantage:
Businesses that effectively leverage their first-party data gain a competitive edge. The ability to offer personalized experiences and targeted marketing campaigns based on real customer insights sets a brand apart in the marketplace.
Compliance and Trust:
First-party data is collected directly from customers with their consent, which helps businesses adhere to data protection regulations. Prioritizing privacy and transparency builds trust with customers, which is essential in today's data-conscious environment.

